Esquema
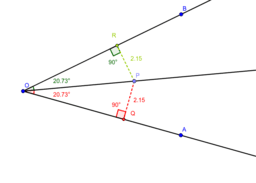
Angle Bisector as a locus. The Incenter of a Triangle
Angle Bisector is the locus of all interior angle points equidistant from the sides of the angle. The three interior bisectors of any triangle meet at a single point, which logically is equidistant from the three sides of the triangle, such that it is the center of the inscribed circle of the triangle, the incenter.