Images for m=0.4. The generalized potential function has the form φ(r)=Σqₖ*|rₖ –r|ᵐ, where m is a real number
The images below were created using an applet. The following explanations will help you to understand the images.
Two types of loci are calculated for each combination of charges. Multifocal closed curves are constructed as follows:
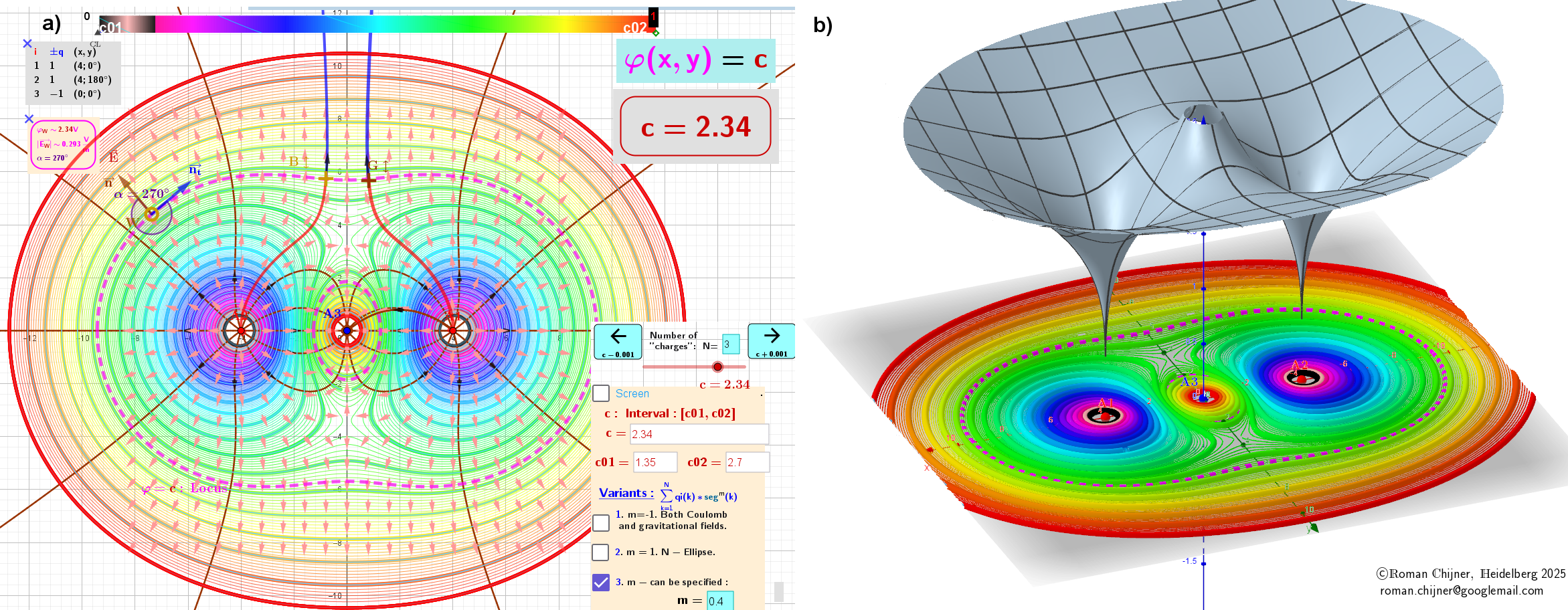
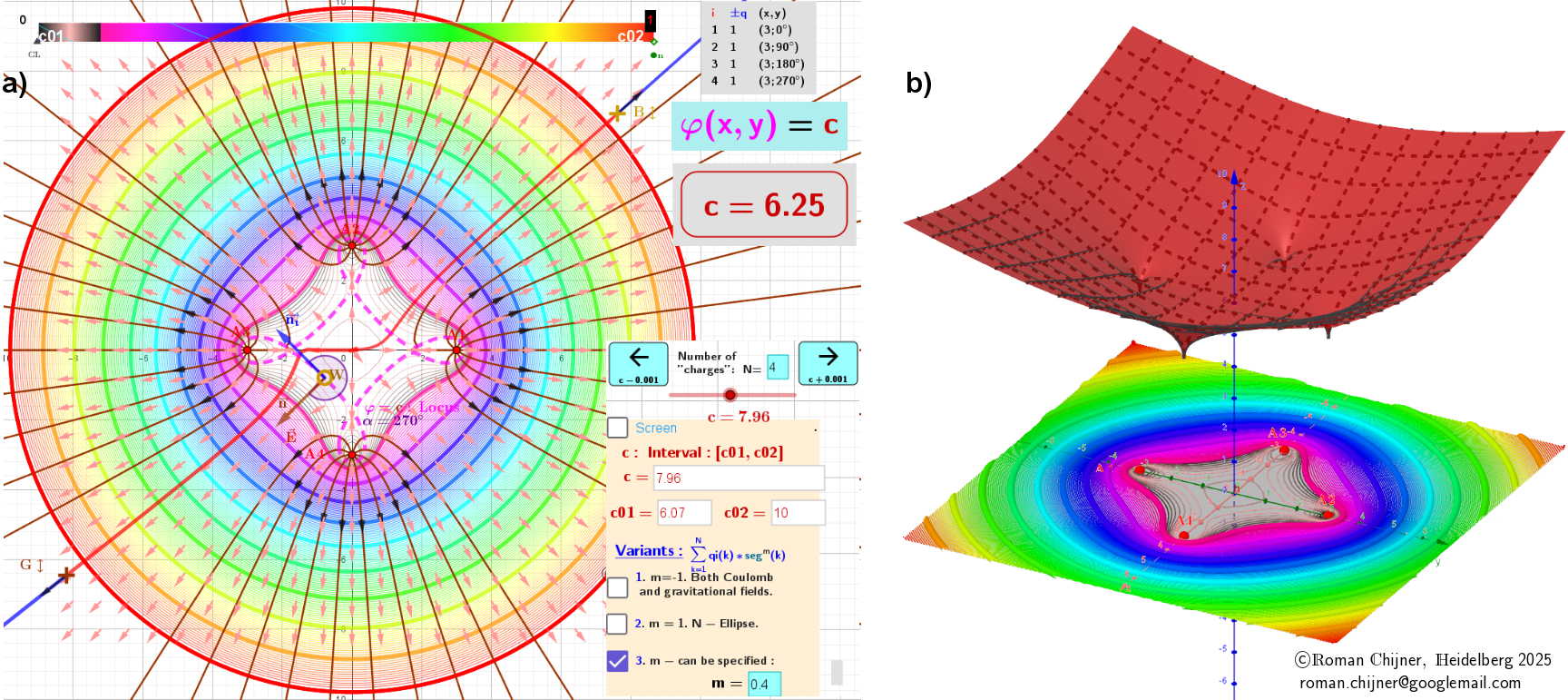
1. The first case corresponds to equipotential lines, φ =c, and the
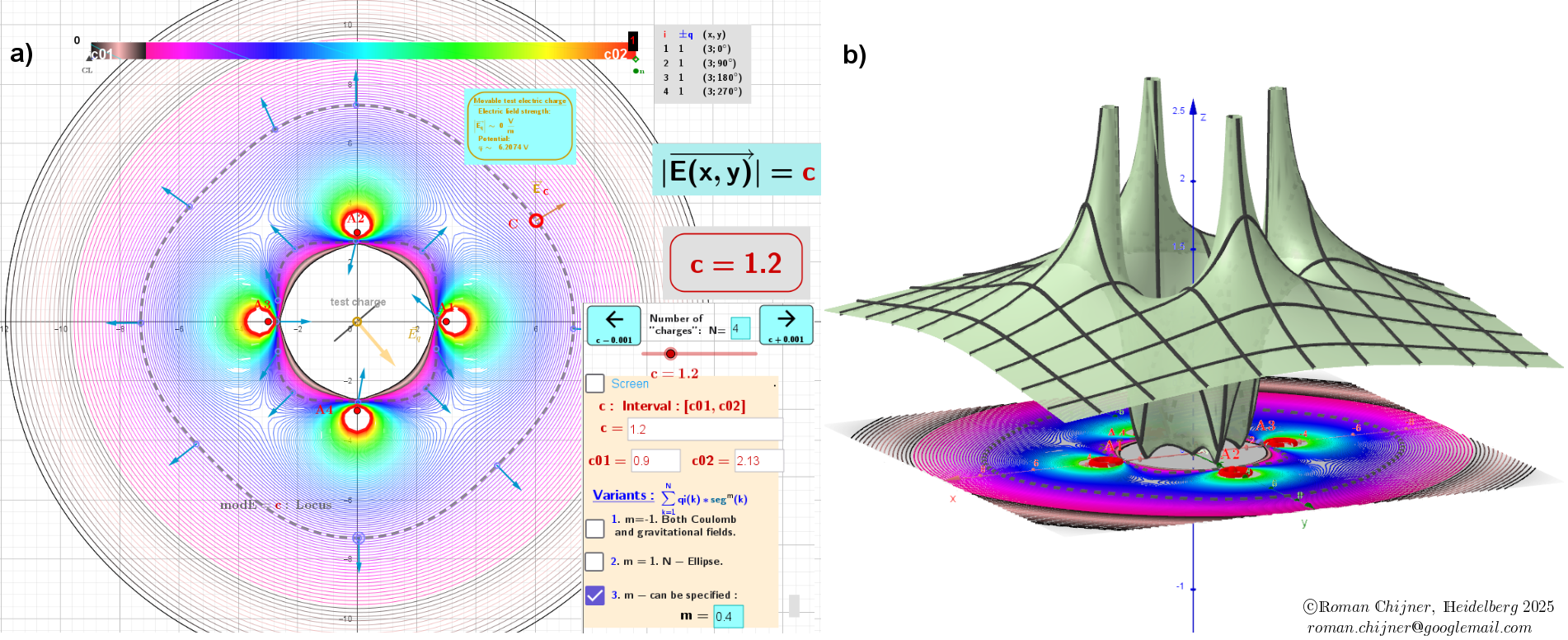
2. The second case corresponds to lines of equal values of the vector field, modE= c.
The variable c lies within the interval c∈[c₀₁,c₀₂], and the boundaries are set manually so that all curves lie within the observation area.
The Heatmap in contour diagrams visualizes the distribution of potential φ (in case 1) and for the field E -value modE (in case 2).
Each case is supported by two images a) and b).
1. For the first case:
a) Contour diagram. Equipotential lines (closed curves of locus φ = c). For a gradient field, these lines are always perpendicular to the vector field lines E. The directions of the vector field at each point in the field are shown by arrows and vector field lines drawn around each charge.
(b) The potential φ(x, y) is represented in three-dimensional space, where positive height corresponds to positive potential φ and negative height corresponds to negative potential.
2. For the second case:
a) Contour diagram: Lines of constant field value (closed curves of the locus modE = c). The value of the vector field is the same on each curve, but the directions are different.
(b) The distribution of vector field values is represented as a surface modE(x, y) in three-dimensional space.
Figure 1: Linear chain of three charges with equal magnitudes but alternating signs
First case: The potential field φ around charges
Second case: The modulus, modE, of the Gradient field E around charges
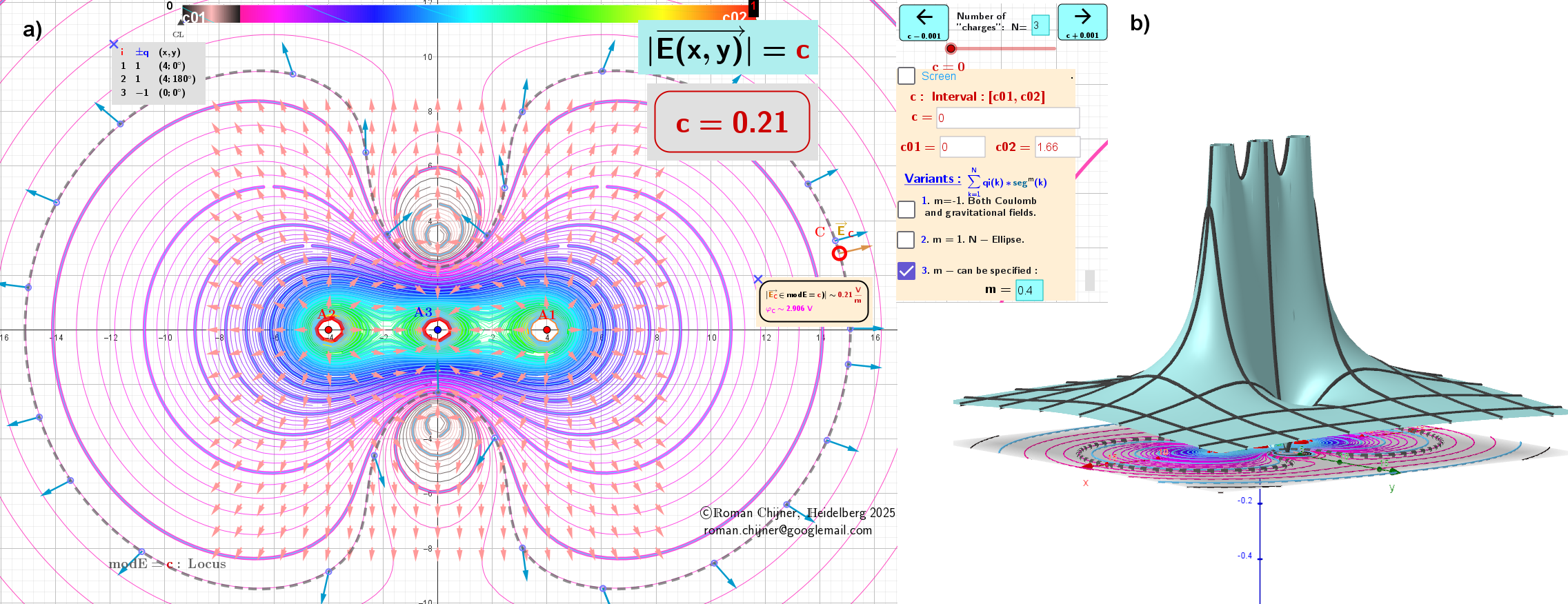
Figure 2: Four charges of equal magnitude and sign are located at the corners of a square
First case: The potential field φ around charges
Second case: The modulus, modE, of the Gradient field E around charges