8.2 Differentiation in Kinematics of Linear Motion
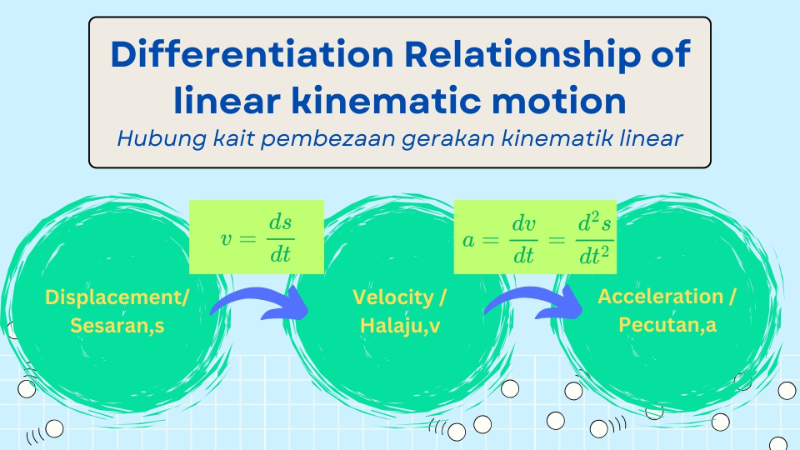
Differentiation in linear kinetic motion refers to the mathematical process of determining the rate of change of motion-related quantities, such as displacement, velocity, and acceleration, with respect to time. These rates are foundational in understanding the dynamics of objects in linear motion. The differentiation always starts from displacement, s=f(x). The velocity is defined as the rate of change of displacement with respect to time. Hence, the velocity function,v is given by:
The acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. Hence, the acceleration function,a is given by:
The relationship between the displacement function, s, the velocity function, v, and the acceleration function, a, can be summarized as shown in the following diagram: