Finding images with a transparency
Isometries with other tools
Dynamic mathematics provides an excellent environment for deep investigation of congruence transformations. There are, however, other tools that offer rich opportunities for exploration and discussions appropriate for lower grades.
Reflections can be explored using
- Semi-transparent mirror
- Paper folding and cutting
- Transparency
- Square dot or square grid paper,
Method 1: A Transparency and marker
A transparency and marker provide a quick way to visualize images resulting from all four isometries. In this activity, practice using them for translation, rotation and reflection.
1.1 Translation
On a blank sheet of paper, draw a shape and place a vector. The shape should have no symmetry, letter "F" is a good example. Explain in detail how you use the transparency to visualize the position of the image of your shape (pre-image) under the given translation.
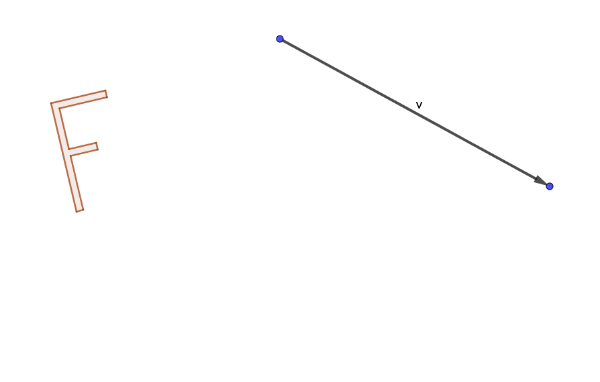
1.1.1 What exactly are you doing to make sure that the translated image is in the correct direction and distance from the pre-image?
1.1.2 What exactly are you doing to make sure that there is no random rotation involved as you "slide" the transparency?
1.2 Rotation
On a blank sheet of paper, draw a shape, mark the center of rotation and decide on its angle. The shape should have no symmetry, letter "F" is a good example. It is fine to visually estimate the angle of rotation. No need to use a protractor or precise construction.
Explain in detail how you use the transparency to visualize the position of the image of your shape (pre-image) under the given rotation.
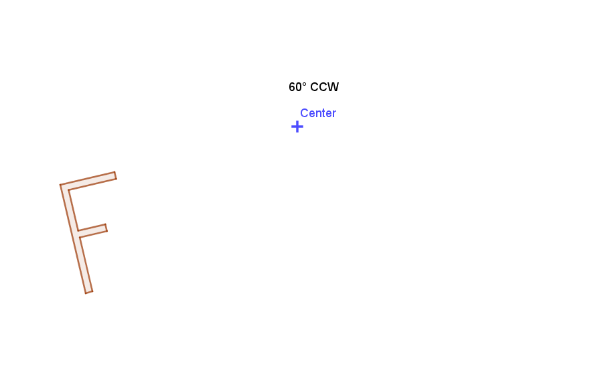
1.2.1 What exactly are you doing to ensure that the rotation will be around the given center?
1.2.2 What exactly are you doing to visualize and keep track of the angle of rotation?
1.3 Reflection
On a blank sheet of paper, draw a shape and line. The shape should have no symmetry, letter "F" is a good example.
Explain in detail how you use the transparency to visualize the position of the image of your shape (pre-image) under the given reflection.
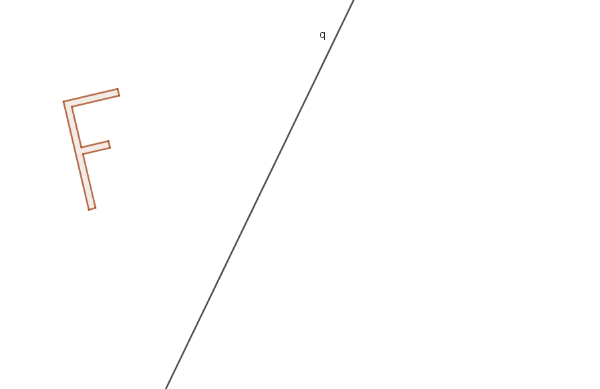
1.3.1 What exactly are you doing to ensure that the pre-image is reflected around the given line?
1.3.2 What exactly are you doing to ensure that there is no random "slide" or "turn" involved when reflecting the pre-image?
2. Semi-transparent mirror (a "Mira" device).
A Semi-transparent mirror allows us to see the reflection of objects in front of the mirror, as well as objects behind it. It is easy to make using a flat, polished and sturdy piece of transparent plastic that partially reflects the light. Containers made of thicker plastic often work.
Semi-transparent mirror is used to draw reflection images. "Mira" devices that are designed to be placed perfectly perpendicularly to the plane of the paper. At home, if you are able to find a suitable piece of plastic, make sure to keep it perpendicular to the paper and experiment with the lighting: Use a lamp or try different positions with respect to window(s) until you see a good reflection.
Semi-transparent mirrors can be used to find lines of symmetry or to draw images under the line reflection. Some examples can be seen here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iY6tSY_1dpI .