Events and Probability
ENGAGE 1
Imagine you have a box containing 10 sticks, and one of them is marked as a winning stick. You are about to draw one stick at random from the box. a. What is the probability of drawing the winning stick?
ENGAGE 2
Explain why each stick has an equal chance of being chosen.
What is probability?
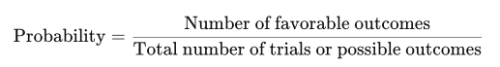
What is "trial"?
What is an "event"?
- Event A: “Rolling a 1” → A = { 1 }
- Event B: “Rolling an odd number” → B = {1, 3, 5}
- Certain events always occur
- Impossible events: never occur (empty set ∅)
- Elementary events: contain only one outcome
What’s the Difference Between Experimental and Theoretical Probability?

- Experimental probability = What did happen
- Theoretical probability = What should happen (in theory)
EXPLORE
Test 1
A bag contains 4 red, 3 blue, and 3 green marbles. One marble is drawn at random. What is the theoretical probability of drawing a blue marble?
Test 2
A "trial" in probability means repeating the same action under different conditions.
Test 3
You roll a standard 6-sided die. List the sample space and write the set representing the event “an even number is rolled.” a. Sample Space (U) : { } b. Event A (even number) : { }
Test 4
You flip a coin once. What kind of event is “getting heads”?
Test 5
You draw a card from a standard deck. You say: "The probability of drawing a heart is 1/4\ because there are 4 suits." Is this statement an example of theoretical or experimental probability? Why?